Reflection and Refraction
🔖 Topics
- Geometric optics
- Reflection
- Plane mirrors
- Refraction
- Total internal reflection
- Apparent depth
🎯 Objectives
- Describe the path that light takes as it travels within and between homogeneous media
- Utilize Snell's law to calculate how much light "bends" at an interface
- Calculate the angle at which total internal reflection occurs
- Solve a variety of problems related to geometric optics
📋 Sequence
- Wavefronts
- Huygen’s Principle
- Reflection by a Plane Mirror
- Example: Two Plane Mirrors at \( 90^\circ \)
- Example: Minimum Height of a Plane Mirror
- Refraction of Light
- Example: Snell’s Law at a Surface
- Example: Snell’s Law in a Thin Film
- Total Internal Reflection
- Example: Water / Air TIR
- Apparent Depth
- Example: Water / Air Apparent Depth of Fish
🖥️ Animations, Simulations, Activities
📝 Practice Problems
- The index of water is 1.33. What is the speed of light in water? What is the wavelength of light in water if it has a vacuum wavelength of 515 nm?
- Unpolarized light is incident on a system of three ideal polarizers. The second polarizer is oriented at an angle of \( 30^\circ \) with respect to the first, and the third is oriented with an angle of \( 45^\circ \) with respect to the first. If light exits the system of polarizers with an intensity of \( 23 \: W/m^2 \), what is the intensity of the incident light?
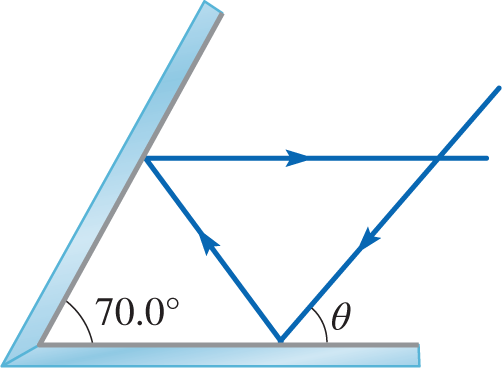
- Two plane mirrors form a \( 70^\circ \) angle as shown in the diagram. For what angle \( \theta \) will the outgoing ray be horizontal?
- A ray of light strikes an air / water interface at an angle of \( 25^\circ \) with respect to the vertical. At what angle, with respect to the vertical, will the light move through the water? The index of refraction of water is 1.33.
- A glass lens has a scratch-resistant plastic coating on it. The speed of light in the glass is 0.67c and the speed of light in the coating is 0.80c. A ray of light in the coating is incident on the plastic-glass boundary at an angle of \( 12^\circ \) with respect to the normal. At what angle with respect to the normal is the ray transmitted into the glass?
- Calculate the critical angle for sapphire surrounded by air. The index of refraction for sapphire is 1.76.
- A defect in diamond appears to be 2.0 mm below the surface. If the index of refraction of diamond is 2.42, how far below the surface is the defect actually located?
- Why does a diamond sparkle less under water than in air?
Challenge Problem
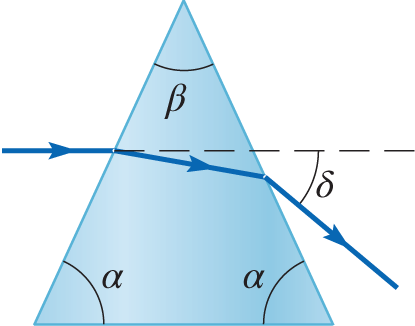
A horizontal light ray is incident on a crown glass prism as shown in the figure. The angle \( \beta = 30^\circ \) and the index of refraction of the crown glass is n = 1.50. Calculate \( \delta \), also called the angle of deviation.
✅ Partial Solutions
- \( 2.26 \times 10^8 : m/s \); \( 387.2 \: nm \)
- \( 65.7 \: W/m^2 \)
- \( 40^\circ \)
- \( 18.5^\circ \)
- \( 10^\circ \)
- \( 34.6^\circ \)
- 4.84 mm
📘 Connected Resources
- Giambattista, Alan, et al. College Physics With an Integrated Approach to Forces and Kinematics. 5th ed., McGraw-Hill Education, 2020.